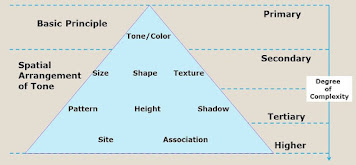
Image Interpretation Elements
- Size
- Shape
- Shadow
- Tone/Color
- Texture
- Pattern
- Height & depth
- Site
- Association
Color
Tone
It refers to the average brightness of an area or, in the case of color imagery, to the dominant color of the region. It depends on the nature of the surface and illumination. Smooth surfaces behave like specular reflectors, they tend to reflect radiation in a single direction. These features may appear bright or dark.
Whereas Rough surfaces behave as diffuse reflectors and Scatter radiation in all directions. Tone is also very important element for interpretation in panchromatic images (Black and White satellite image).
Size
- Relative size determined by comparing the object with familiar nearby features. Relative size is important in differentiating between objects.
- For example during the interpretation of land use map than differentiating residential, commercial and industrial features becomes very easy by deploying relative size concept as industry and commercial building features are comparatively bigger in size with respect to residential buildings.
- Absolute size refers to derive measurements by using satellite images/aerial photographs. In this process absolute size of object is measured by multiplying length. But accuracy of measurement depends upon the accuracy of geometric correction.