GPS (Global Positioning System)
GPS is a satellite-based navigation system used to determine the location on land, sea, and in the air around the Earth. GPS is developed by the U.S. Department of Defense. It provides accurate information about location (such as cities, villages and buildings etc.), velocity and time synchronization. It operates through a network of at least 24 satellites orbiting the Earth, working with ground stations and receivers to deliver real-time positioning services.
For example, Location of schools, hospitals, offices and climate data (rainfall data, temperature data) etc. can be collected using GPS and could be integrated with GIS for further spatial data generation and data analysis. By using these locations, one can measure the distances between two locations as well as can estimate the travel time.
How Do GPS Works
GPS consists of three segments: 1. Satellites 2. Ground Stations 3. Receivers
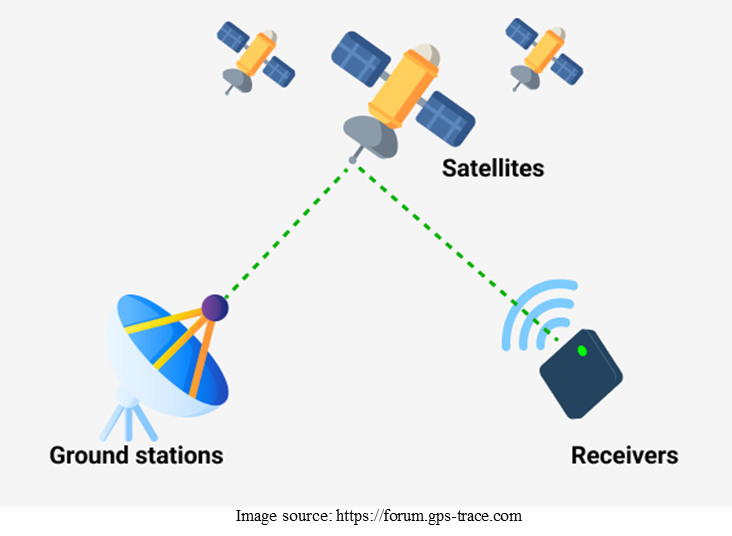
- Satellites or space segment:
- It consists of 24+ satellites orbiting Earth and ensure global coverage.
- Ground stations or control Segment:
- Ground stations monitoring the satellites and manage satellite health and trajectory.
- Receivers or user segment:
- Devices like smartphones, GPS trackers, and vehicles receives satellite signals to determine the location.
- GPS receivers requires signals from at least 3 satellites for 2D positioning (latitude and longitude), however requires 4 satellites for 3D positioning (latitude, longitude, and altitude).
GPS Applications
Navigation: GPS is used in cars for route planning, real-time traffic updates, and turn-by-turn directions. Also assists in plotting sea routes and ensuring safe navigation for ships and boats. However, in aviation industry it helps pilots with flight navigation, accurate landing, and tracking of aircraft. Assists in military mission planning and troop movements. Also enhances precision in missile guidance and reconnaissance operations. Now a days GPS is also used to for tracking satellites and spacecraft navigation.
For example: Google Maps for daily commutes and road trips. In aviation industry, aircraft autopilot systems use GPS for precise navigation. Cargo ships use GPS for ocean navigation to avoid hazards. Fishing vessels rely on GPS to locate prime fishing areas.

Transportation and Logistics: Various companies use GPS to track vehicles, monitor driver behavior, and optimize delivery routes. Apps like Uber, Ola etc. rely on GPS for driver and passenger location matching. GPS is also used for real-time tracking of buses, trains, and taxis to improve the operational efficiency and passenger updates. GPS reduces operational costs in logistics and transportation.
For example: Logistics companies like FedEx tracking shipments worldwide using this technology. Ride-hailing apps like Uber rely on GPS for efficient pickup and drop-off.
Location-Based Services: GPS enables apps like Google Maps, food delivery services, and social media check-ins. It simplifies the daily tasks like navigation and activity tracking.
For example: Delivery services like Amazon optimizing routes for faster deliveries.
Land Surveying and Mapping: GPS provides precise measurements of land parcels, property boundaries and construction projects. Facilitates the creation of accurate maps for various applications such as landuse/landcover mapping, urban planning etc.

Urban and Infrastructure Development: GPS helps in designing roads, utilities, and public spaces. Assists in construction project progress monitoring, check encroachment and ensuring precision.
For example: Highway and bridge construction, designing smart cities like Singapore.
Agriculture: GPS enables efficient monitoring of crop health and resource allocation. It helps farmers optimize planting, fertilizing, and harvesting operations with pinpoint accuracy.
For example: GPS-guided tractors are used for planting and harvesting with precision. GPS in agriculture allows farmers to precisely navigate to specific locations in the field to collect soil samples or monitor crop conditions such as one can map pest, insect, and weed infestations in the field. This real time data can be integrated with remote sensing and GIS for pest detection.
Emergency Services: GPS aids in locating people during natural disasters or accidents and allows emergency services to pinpoint caller locations for faster response times. It enhances public safety by improving emergency response and disaster management.
For example: GPS helps to locate flood or earthquake-affected regions and deploying aid. Ambulances using GPS for the fastest routes to hospitals. GPS devices could be used in mountain rescue operations to locate hikers.
Tourism: Assists travelers in finding attractions, hotels, and restaurants.
Environment Monitoring: GPS is used for wildlife tracking such as GPS tags are used to monitor animal movements and to study migration patterns. Also helps in mapping deforestation, glacier movements, and ocean currents.
For example: Tracking deforestation using GPS-enabled drones

Typical GPS Accuracy Levels
| Technology | Accuracy | Use Case |
| Standard GPS (L1 only) | 5–10 meters | Consumer devices, navigation apps |
| Differential GPS (DGPS) | 1–3 meters | Surveying, maritime navigation |
| Assisted GPS (A-GPS) | 5–10 meters (faster fix) | Smartphones, urban navigation |
| Dual-Frequency GPS | 30 centimeters–1 meter | Advanced mapping, high-end smartphones |
| Real-Time Kinematic (RTK) GPS | 1–2 centimeters | Precision farming, land surveying |
| Military GPS | Sub-meter accuracy | Military applications (e.g., missile guidance) |
The important information related to GPS has been shared in this article including the defining GPS, process of GPS working, and application of GPS in different fields.