Raster Data Formats used in GIS and Remote Sensing
- Raster
- Vector
RASTER DATA
Representation of Raster Data
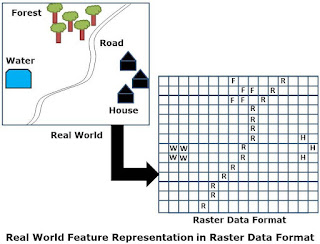
Raster data representation of Features
- Points features by single cells
- Line by sequence of neighboring cells
- Polygons by collections of contiguous cells
Organization of Raster Data
Raster Coding
Advantages of Raster Data Model
- Raster data model is capable to represent different types of continuous surfaces. Such as Topography, land use/land cover, air quality, ground water pollution level etc. can be stored at raster layers.
- Raster data model support fast computer processing. Such as fast display of surface data, ability to handle very large databases, Tiling, Compression to reduces storage requirement.
- Many spatial and modeling applications work only on data in raster format. For example, hydrologic modeling such surface runoff modeling, elevation modeling and pollution modeling
- Remote Sensing Data are the major source for input data in analysis is based on raster data model.
Limitations of Raster model
- Rater data model is not suitable for applications that rely on individual spatial features represented by points, lines and polygons. For example network analysis.
- Precise locations may not be recorded in raster data as compare to vector data.
- Features are usually generalized in raster data and do not appear as cartographically pleasing as vector data.
- Resolutionof raster data determines applicability of raster data. With the increase in resolution it increase data volume and affect the computer processing speed.
V V meaningful
V beneficial information n
Nice message
When your website or blog goes live for the first time, it is exciting. That is until you realize no one but you and your. Work from home jobs